The essential technique of immunoblotting, or Western blotting, is indispensable. Nearly every paper published in the area of molecular biology uses western blotting to detect specific proteins in tissue homogenates or cell lysates. You can look for the best western blotting service via https://www.bosterbio.com/services/assay-services/western-blotting-service.
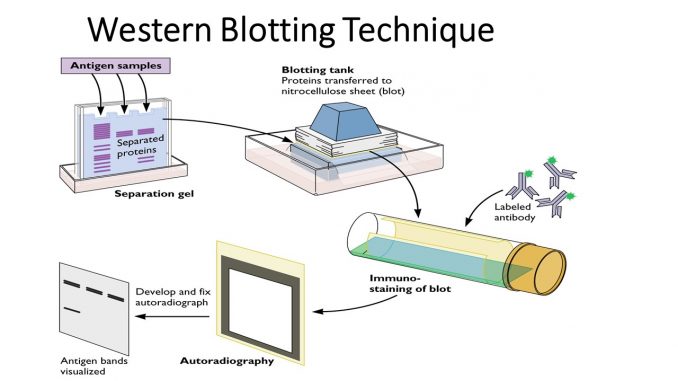
Image Source: Google
Western blotting uses the resolving power or SDS-PAGE of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to combine with the specificity of antibodies to detect target protein.
The molecular weight of proteins is determined in SDS-PAGE. They are then transferred from the polyacrylamide gel onto membranes (Nitrocellulose and PVDF), creating an exact copy of the pattern of protein separation on the membrane.
After the proteins have been transferred to the membrane, it is necessary to ‘block’ any non-specific binding spots on the membrane’s surface. Bovine Serum Albumin or Skimmed milk, or purified milk Casein are used to block the membrane.
G-Biosciences recommends any of these blocking agents to block the membranes. The absence of blocking antibodies can bind to non-specific binding sites on membranes and make it difficult for the target protein to be detected, leading to false positives.
After proteins are immobilized on the binding surface and have been blocked, they can then be probed using a primary antibody that is specific for the protein in question.
You can detect bound or absorbed proteins with either a primary antibody that is coupled to a reporter molecule or a secondary antibody that is coupled to the reporter molecules such as Horseradish peroxidase and a fluorophore.